Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT): A key Target In Tumor Research
Three American scientists were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for revealing the molecular mechanism by which telomeres and telomerase protect chromosomes in October 5, 2009. This discovery not only answered the core question of how cells combat aging, but also opened up a new path for cancer treatment.

Telomeres are special DNA-protein complexes located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, composed of highly conserved repetitive sequences (in humans, it is TTAGGG) and their associated proteins.
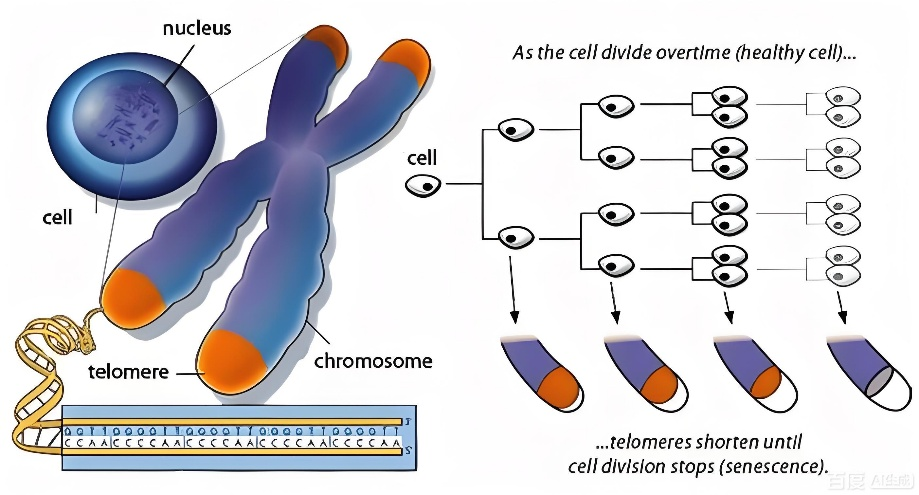
The three core functions of telomeres are:
1, Structural protection: Preventing the chromosome ends from being recognized as DNA damage.
2, Replication compensation: Solving the "end-replication problem" to avoid loss of genetic information.
3, Cellular clock: Regulating the limit of cell division (Hayflick limit) through length changes.
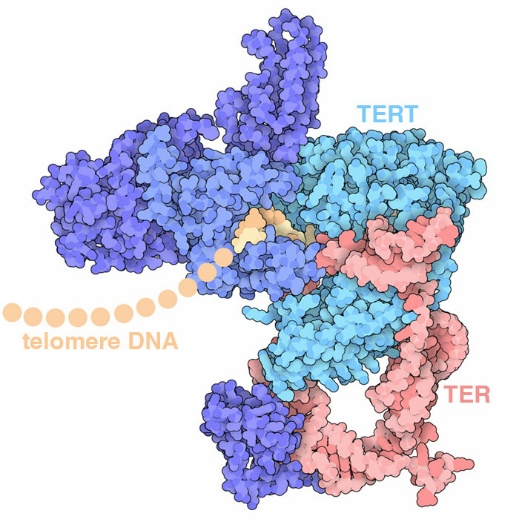
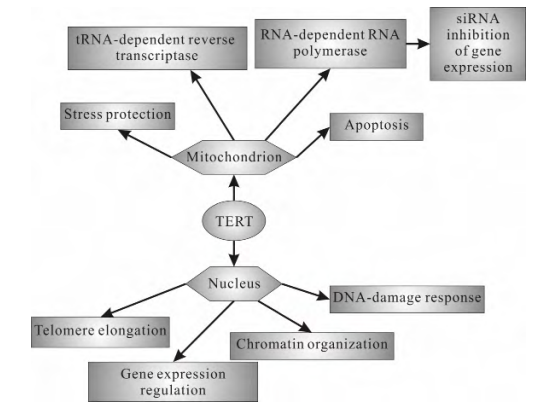
TERT, as the core catalytic subunit of telomerase, is responsible for reverse transcribing the sequence of telomeric RNA (hTR) and adding it to the chromosome ends, thereby compensating for the shortening of telomeres caused by cell division. This mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining chromosomal stability and cell immortalization. Because TERT expression is inhibited in normal somatic cells, telomeres gradually shorten; while 85-90% of tumor cells achieve "immortality" through reactivation of TERT, making it one of the core targets in tumor biology research. The latest review in the "Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer" states:
1, Lung cancer risk: Shortening of telomeres increases the risk of lung cancer by 3.15 times (OR = 3.15, 95% CI: 2.12 - 4.67).
2, Prognostic marker: The length of telomeres in tumor tissues is an independent prognostic factor for early NSCLC (HR = 2.67).
3, Driver gene: The TERT rs2736100-C allele is significantly associated with EGFR mutations.
The detection of Telomerase technology:
1. TRAP method (Telomere Repeat Amplification Protocol)
· Principle: Through PCR amplification of the repetitive sequences synthesized by telomerase, combined with gel electrophoresis or fluorescence quantitative analysis to determine the amount of the product.
· Advantages: High sensitivity (can detect a small number of cells), strong specificity.
· Limitations: The operation is cumbersome, PCR contamination needs to be prevented, and radioactive labeling or fluorescent dyes are required.
2. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
· Principle: Utilize fluorescent probes to monitor the amplification process of telomerase extension products in real time, and calculate the activity quantitatively.
· Advantages: No need for electrophoresis, high automation, suitable for high-throughput detection.
· Limitation: Specific primers need to be designed, and reaction conditions must be strictly controlled.
3. Immunological detection
· Principle: Capture the telomerase protein components (such as the catalytic subunit of TERT) with antibodies, combined with ELISA or Western blot for quantification.
· Applicable scenarios: Rapid screening of a large number of samples, but only reflects protein expression levels, and cannot directly reflect enzyme activity.
We DLdevelop.Inc have high stability and quality elisa kits for research use. We will always provide the best service for our clients all over the wold!

Telomeres are special DNA-protein complexes located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, composed of highly conserved repetitive sequences (in humans, it is TTAGGG) and their associated proteins.

The three core functions of telomeres are:
1, Structural protection: Preventing the chromosome ends from being recognized as DNA damage.
2, Replication compensation: Solving the "end-replication problem" to avoid loss of genetic information.
3, Cellular clock: Regulating the limit of cell division (Hayflick limit) through length changes.


TERT, as the core catalytic subunit of telomerase, is responsible for reverse transcribing the sequence of telomeric RNA (hTR) and adding it to the chromosome ends, thereby compensating for the shortening of telomeres caused by cell division. This mechanism plays a crucial role in maintaining chromosomal stability and cell immortalization. Because TERT expression is inhibited in normal somatic cells, telomeres gradually shorten; while 85-90% of tumor cells achieve "immortality" through reactivation of TERT, making it one of the core targets in tumor biology research. The latest review in the "Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer" states:
1, Lung cancer risk: Shortening of telomeres increases the risk of lung cancer by 3.15 times (OR = 3.15, 95% CI: 2.12 - 4.67).
2, Prognostic marker: The length of telomeres in tumor tissues is an independent prognostic factor for early NSCLC (HR = 2.67).
3, Driver gene: The TERT rs2736100-C allele is significantly associated with EGFR mutations.
The detection of Telomerase technology:
1. TRAP method (Telomere Repeat Amplification Protocol)
· Principle: Through PCR amplification of the repetitive sequences synthesized by telomerase, combined with gel electrophoresis or fluorescence quantitative analysis to determine the amount of the product.
· Advantages: High sensitivity (can detect a small number of cells), strong specificity.
· Limitations: The operation is cumbersome, PCR contamination needs to be prevented, and radioactive labeling or fluorescent dyes are required.
2. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
· Principle: Utilize fluorescent probes to monitor the amplification process of telomerase extension products in real time, and calculate the activity quantitatively.
· Advantages: No need for electrophoresis, high automation, suitable for high-throughput detection.
· Limitation: Specific primers need to be designed, and reaction conditions must be strictly controlled.
3. Immunological detection
· Principle: Capture the telomerase protein components (such as the catalytic subunit of TERT) with antibodies, combined with ELISA or Western blot for quantification.
· Applicable scenarios: Rapid screening of a large number of samples, but only reflects protein expression levels, and cannot directly reflect enzyme activity.
We DLdevelop.Inc have high stability and quality elisa kits for research use. We will always provide the best service for our clients all over the wold!